In today's rapidly evolving industrial landscape, energy efficiency has become a paramount concern. Industries across the spectrum are constantly seeking innovative ways to reduce energy consumption, optimize processes, and minimize environmental impact. Two critical components that play pivotal roles in achieving these goals are Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers and Thermal Fluid Heaters. In this article, we will explore the significance of these technologies, their applications, and how they contribute to enhancing energy efficiency.
Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers: The Efficiency Enablers
Understanding Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
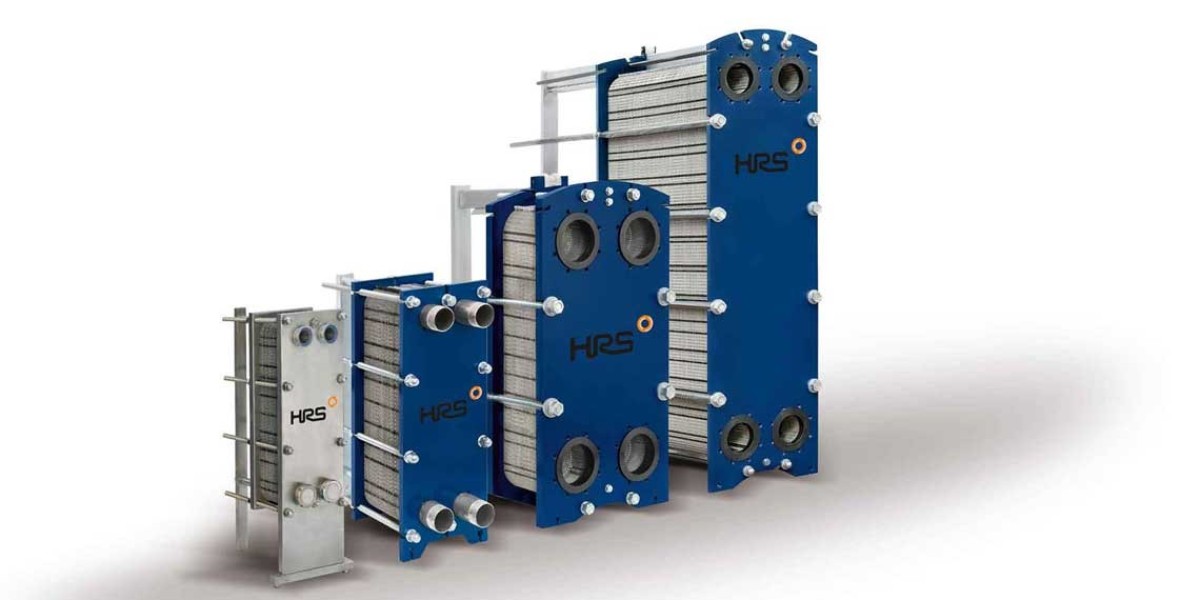
A Gasketed Plate Heat Exchanger (GPHE) is a compact, highly efficient device designed for the transfer of heat between two fluids while keeping them physically separated. The core of this technology comprises multiple thin plates with strategically engineered patterns. These plates are stacked and sealed with gaskets to form a plate pack.
Applications of GPHEs
HVAC Systems: GPHEs are extensively used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to recover energy from exhaust air and preheat incoming fresh air, reducing the overall energy consumption of the building.
Industrial Processes: In various industrial processes such as food and beverage production, chemical manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals, GPHEs facilitate precise temperature control, which is crucial for product quality and process efficiency.
District Heating and Cooling: GPHEs are integral in district heating and cooling systems, enabling the efficient transfer of thermal energy between centralized sources and consumers.
Energy Efficiency Benefits
1. Compact Design
GPHEs are compact and have a high heat transfer surface area per unit volume. This space-saving design reduces the overall footprint and installation costs, making them an attractive choice for industries with limited space.
2. Enhanced Heat Transfer
The unique plate configuration of GPHEs promotes turbulent flow, resulting in excellent heat transfer efficiency. This translates to reduced energy consumption as less power is needed to achieve the desired temperature changes.
3. Easy Maintenance
GPHEs are relatively easy to clean and maintain due to their accessible plate design. Regular maintenance ensures they continue to operate at peak efficiency, minimizing downtime.
4. Scalability
GPHEs are scalable, allowing industries to adapt their heating and cooling systems to changing demands without significant infrastructure modifications. This flexibility contributes to long-term energy savings.
Thermal Fluid Heaters: Precision in Heat Generation
Unveiling Thermal Fluid Heaters
Thermal Fluid Heaters, also known as thermal oil heaters or hot oil heaters, are specialized devices used for the precise and efficient generation of high-temperature heat. They employ a heat transfer fluid (thermal oil) to transport and distribute heat to various processes.
Applications of Thermal Fluid Heaters
Manufacturing: Thermal fluid heaters find extensive use in manufacturing industries such as chemical, plastics, and textiles, where precise temperature control is critical for product quality and consistency.
Oil and Gas: In the oil and gas sector, thermal fluid heaters are employed for heating crude oil during extraction and refining processes.
Food Processing: The food industry relies on thermal fluid heaters to maintain specific temperatures for cooking, frying, and sterilization.
Energy Efficiency Benefits
1. High Heat Transfer Efficiency
Thermal fluid heaters offer excellent heat transfer rates and temperature control, minimizing energy waste. They can reach high temperatures without the risk of overheating or degradation, ensuring consistent and efficient heat generation.
2. Low Maintenance
These heaters have a robust design and require minimal maintenance, reducing downtime and associated energy losses.
3. Versatility
Thermal fluid heaters can be tailored to meet specific temperature and heat transfer requirements, making them versatile for various applications.
4. Closed-Loop Systems
The closed-loop nature of thermal fluid systems prevents heat loss to the environment, further enhancing energy efficiency.
Synergy in Energy Efficiency: GPHEs and Thermal Fluid Heaters
Where the Two Technologies Converge
While Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers and Thermal Fluid Heaters serve different primary functions, they often work in tandem to create comprehensive energy-efficient solutions.
Heat Recovery: GPHEs can recover heat from various industrial processes and transfer it to thermal fluid heaters. The recovered heat can then be used for other processes or heating applications, significantly reducing the need for additional energy sources.
Precise Temperature Control: GPHEs can maintain precise temperature control in the thermal fluid circuit, optimizing the performance of the thermal fluid heater and minimizing energy consumption.
Process Integration: Integrating these technologies into a well-designed system allows industries to maximize energy efficiency across the board, leading to substantial cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Case Studies: Real-World Energy Efficiency
Case Study 1: Brewery Operations
A brewery incorporated GPHEs into its production process to recover heat from wort cooling. The recovered heat was then transferred to a thermal fluid heater, providing consistent and energy-efficient heating for the mashing and boiling processes. This integration reduced the brewery's energy costs by 30% while maintaining product quality.
Case Study 2: Chemical Manufacturing
A chemical manufacturing plant employed GPHEs to recover heat from its distillation process. The recovered heat was directed to a thermal fluid heater, which supplied precise and high-temperature heat for reaction processes. This integration not only reduced energy consumption by 25% but also enhanced production efficiency.
Conclusion
In the quest for enhanced energy efficiency, industries are turning to innovative technologies like Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers and Thermal Fluid Heaters. These technologies, when used individually, bring substantial benefits to various industrial processes. However, their true potential shines when they are integrated into a holistic energy management system, where they complement each other, resulting in remarkable energy savings, reduced environmental impact, and increased competitiveness in today's sustainability-focused market. Embracing these technologies is not just a step towards efficiency; it's a leap towards a more sustainable and profitable future.